A blood pressure monitor is used to track your blood pressure. Blood pressure values could present variations related to daily activities. This is particularly true for those already diagnosed with high blood pressure. So a single measurement per month may not represent your actual blood pressure. In fact some people have blood pressure spikes every time they enter the doctor’s office, the so called “white coat hypertension”. It is advisable to purchase your own blood pressure monitor and learn how to use it correctly.
How to Use a Blood Pressure Monitor
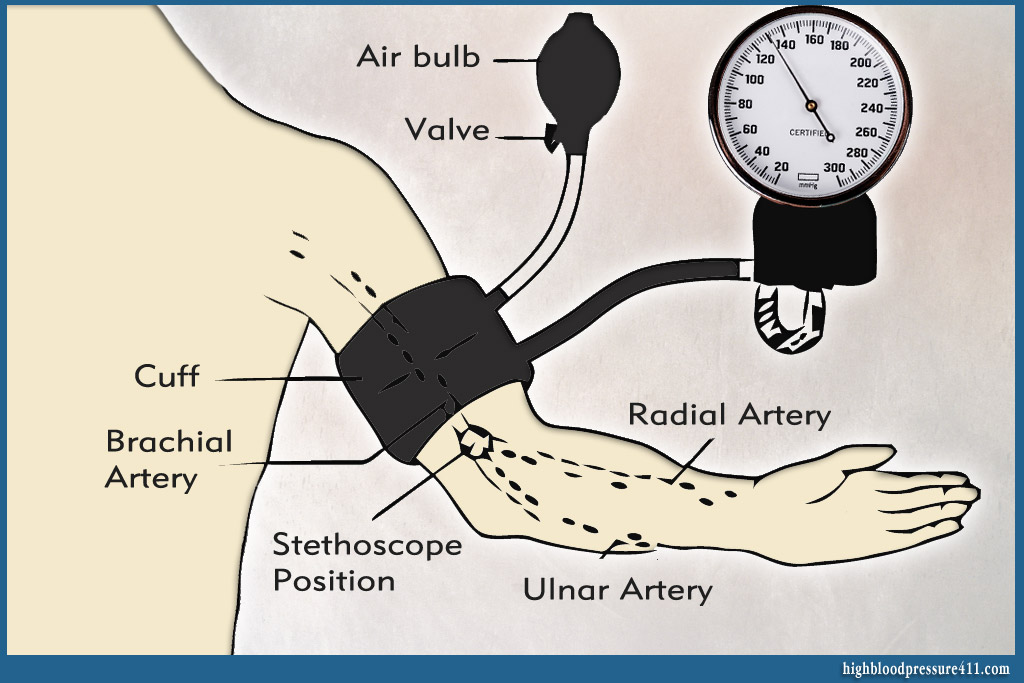
This type of monitor has 3 parts:
- An inflatable cuff – It is applied around the arm. It must be 80-100% of arm circumference
- A measuring unit (a manometer) – It records the numbers of your blood pressure.
- An inflation bulb (to inflate the cuff) – It pumps air inside the cuff.
- The cuff is applied around the arm, 1-2 cm (~1 finger breadth) from the folding part of inside elbow.
- Inflate the cuff with the inflation bulb. This stops the blood flow in the artery for a short time.
- Then release a little the valve of the inflation bulb for the cuff to begin to deflate slowly.
- Place the stethoscope over the artery and listen for the sound of blood as it begins to flow through the artery again.
- Notice when you hear the first sound and look at the manometer. You will observe that the pointer shows a number. This corresponds to the Systolic component of blood pressure.
- This sound will disappear gradually, because the artery is decompressed, as the cuff is deflated. Again notice the number recorded on the manometer by the time you have heard the last sound (this is the Diastolic component of the blood pressure).
They may be inflated manually (with an inflation bulb) or automatically (by simply pressing a button). The basic type of automatic blood pressure monitor has two parts:
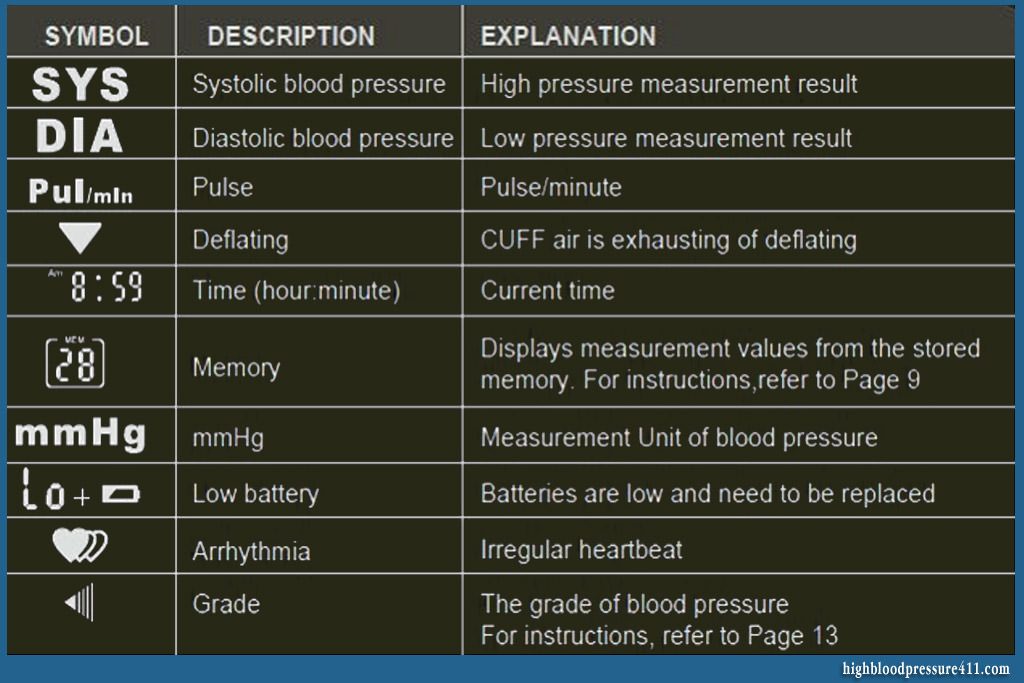
- A digital monitor – It records blood pressure and heart rate.
- A cuff – If may be either an arm or a wrist cuff. The wrist cuff must be placed 1-2 cm away from the wrist and kept at the level of the heart during measurement.
Of note that wrist devices are frequently subject to errors (according to British Association of Hypertension. Those errors result from the incorrect positioning of the arm in relation to the heart.
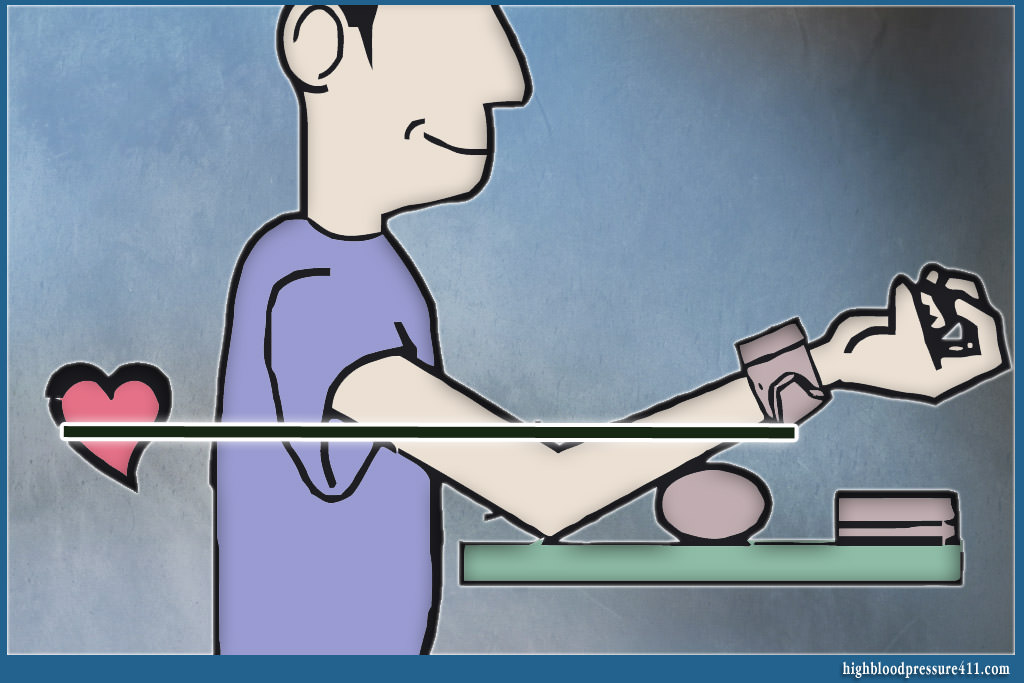

Errors during blood pressure measurement with a wrist device are due to wrong position of the arm in relation to the heart
- A good blood pressure monitor must be Tested and Approved:
Several independent medical associations publish every year the standard features and lists of the qualified blood pressure devices like the Association of Advancement of Medical instrumentation and British Hypertension Society.
- A blood pressure Monitor Easy to Use:
It doesn’t matter what type of device you utilize us long as you don’t know how to use it correctly. You must become familiar with certain basic features of your blood pressure monitor:
- Is it easy to put the cuff?
- Can you read clearly the screen numbers?
- Do you need a sound indicator when your blood pressure is not normal?
- Would you be the primary user of the monitor or you are a caregiver?
- You need a device that can record the time and day that you take the blood pressure measurements?
- Make a list of your needs and requirements before start searching the market.
- You need some technology features:
Wearable technology is comprised by a variety of health tracking devices and applications. You can take measurements of your blood pressure anytime, anywhere without the need of carrying around a bulky device. There are several portable blood pressure monitors that may connect to your mobile phone and keep records of your blood pressure.
- Your doctor knows better: Much information about blood pressure devices is available on the web. To avoid confusion consult your physician with the above questions before proceeding to the purchase.
The Drawbacks of Home Monitoring
- A group of researchers from the University of Alberta have recently tested the accuracy of home blood pressure monitors. They observed that home readings were off almost 70 percent of the time. Apart from this two thirds of the devices took measurements that presented deviations by more than 5 mmHg, which is a considerable difference.
- Because portable blood pressure monitors are tested on healthy people, could not be as accurate in people who have vascular disease.
- Home blood pressure device measurement should be compared with a blood pressure measurement by your GP before become confident with home blood pressure readings.
- Multiple blood pressure readings are required for diagnosis and proper treatment decisions. Canadian guidelines on blood pressure monitoring, recommend 28 measurements over one week for home devices.
Download the printable Blood Pressure Tracking Chart