High blood pressure is reciprocally related to stroke. Its occurrence increases the risk for stroke and certain types of strokes may end up with high blood pressure due to eventual damage to brain centers that participate in blood pressure control.
Stroke occurs when blood flow to a certain brain region is compromised. This could happen because the blood vessel(s) responsible for blood supply of that brain part are either damaged or defective. The resulting symptoms are related to the affected part of the brain. If for example, the involved brain region is responsible for speaking, then speech impairment will appear.
How High Blood Pressure can cause stroke?
Brain blood vessel rupture : Extremely high blood pressure spikes could stress brain arteries leading to rupture and bleeding. This is the so called hemorrhagic brain stroke.
Brain blood vessel clogging : Chronically increased blood pressure, can cause damage to the brain blood vessel walls, rendering them more susceptible to clogging. That’s because platelets and white blood cells tend to accumulate to the site of damage in order to heal the damaged arteries. This could be the cause of an ischemic brain stroke.

Brain blood vessels become clogged as a result of cholesterol plaques or blood clots, which stop or decrease blood flow towards a certain part of the brain.
Causes of ischemic stroke:
- Heart disease particularly valve disease
- Irregular heart beat – Atrial fibrillation is a common type of arrhythmia which facilitate clot formation.
- High blood cholesterol leads to plaque formation with subsequent blood vessel narrowing.
- High blood pressure could lead to rupture of cholesterol plaques.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when blood flow to a certain part of the brain stops for seconds. It causes symptoms similar to stroke but of short duration and without aftereffects. Beware that TIA’s may precede a stroke or could be manifestations of a serious blood disorder or a vascular disease.
What is Hemorrhagic Stroke?
Brain blood vessels rupture due to high blood pressure, resulting in regional brain bleeding. Hemorrhagic stroke is uncommon situation comprising about 15% of all brain strokes but is the cause of death for 40% of them.
There are two types of brain hemorrhage that can cause stroke:
Intracerebral hemorrhage : Vessel bleeding occurs inside a certain region of the brain affecting the corresponding function for which this region is responsible for. That is because blood flow to that part of the brain is compromised.
Causes of intracerebral hemorrhage include:
- High blood pressure
- Blood vessel aging
- Arteriovenous malformations
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs outside the brain tissue, between brain and its protecting covering, a strong membrane called arachnoid mater. The spilled blood accumulates in the space in between, exerting pressure to the whole brain tissue.
Causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage include:
- Head trauma
- Blood thinners
- Bleeding disorders
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) ; An AVM is a mesh of blood vessels that connects arteries and veins in the brain, disrupting the normal oxygen transport. It is very rare and most often is congenital.
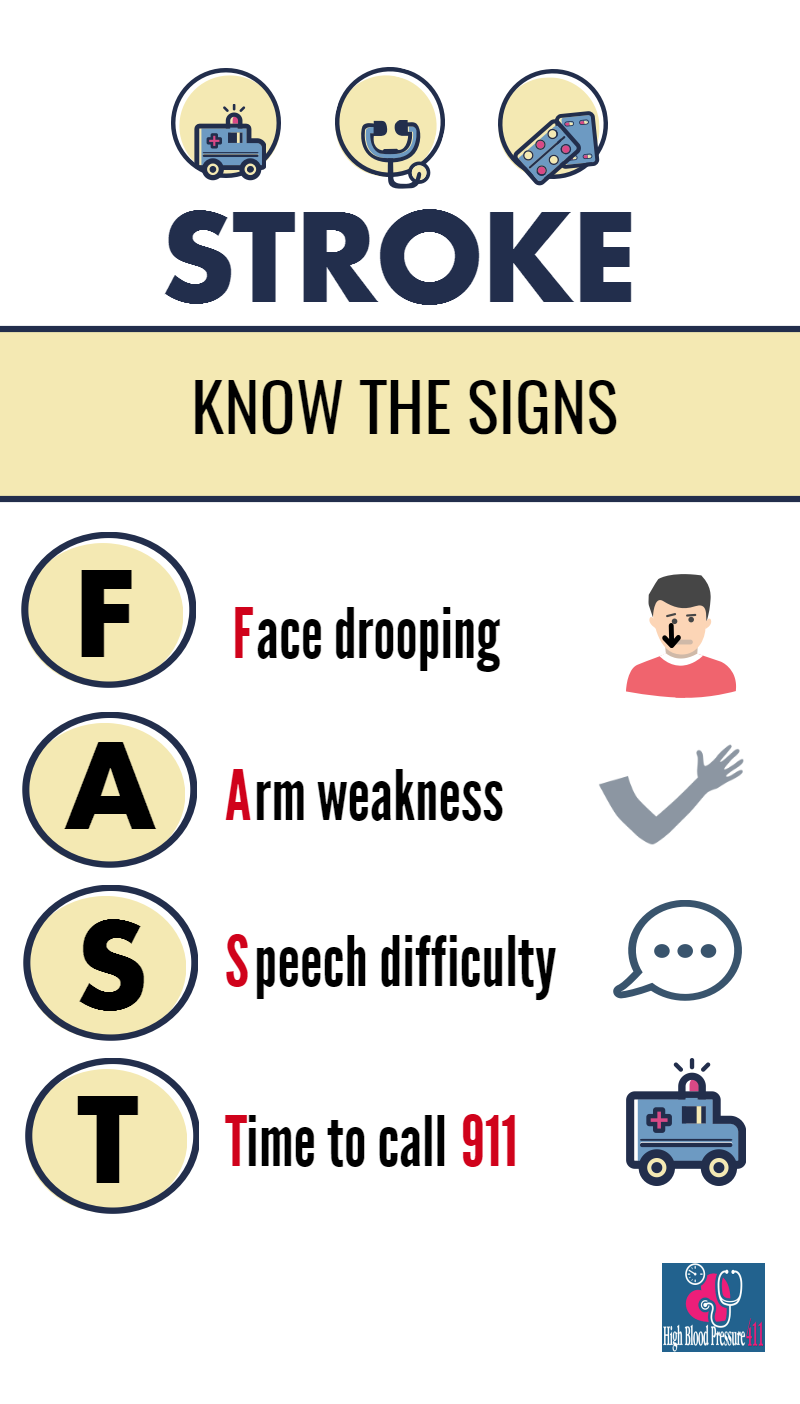
What to do if you suspect a Stroke
- Call 911 immediatelly. Even if the symptoms quickly dissapear, this doesn’t mean that the stroke isn’t still on the way.
- Note how much time has passed since the first stroke signs appeared.
- This information will be of great value for the physicians to decide which kind of treatment would be appropriate for the patient. That is because some medications for stroke are effective only when given during a certain time interval after its onset.
- Check pulse and if not present, start CPR.
- Do not give the person to eat or to drink. Do not give any type of medication. Giving an aspirin to a person that could have a hemorrhagic stroke (i.e. ruptured brain vessel) is not a good idea. You will not know what kind of stroke it is until you arrive in ER and a CT scan is done.
References
-
- Understand stroke – National Stroke Association
- How high blood pressure can lead to stroke – American Heart Association